Lighting fixtures that use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as light sources have gradually begun to penetrate the market due to their low power consumption and long life. Among them, bulb-type LED lighting (hereinafter referred to as LED bulbs) intended to replace traditional bulbs such as incandescent bulbs and bulb-type fluorescent lamps has recently received much attention. Since the price per unit time of the bulb calculated according to the LED lifetime is already comparable to that of the traditional bulb, it is expected to accelerate the popularity in ordinary households.
The first manufacturer to introduce low-cost LED bulbs is Sharp. Sharp entered the LED bulb market with a low price of less than 4,000 yen. This price setting is very impactful, about half the market price of LED bulbs at that time. Toshiba Lighting (Toshiba LighTIng) responded quickly, and 11 days after Sharp's product launch, it released new low-cost LED bulb products * 1 and * 2 with Sharp.

Figure 1: Low-cost LED bulbs Toshiba Lighting and Sharp have successively launched ordinary bulb-type LED lighting (LED bulbs) whose price is about half that of the past, with a retail price of less than 4000 yen. In order to prevent the decline in luminous efficiency and shorten the life, LED heat dissipation is very important. Therefore, the lower part of the LED bulb is a radiator made of aluminum alloy castings
The lower part of the bulb is a heat sink
Low price does not mean that LED bulbs can abandon the unique advantages of low power consumption and long life. Moreover, if the product is to be based on the market, it also needs to have a high heat dissipation capacity.
The light emitted by the LED bulb has little infrared component. Therefore, compared with incandescent bulbs and bulb-type fluorescent lamps, the temperature rise of the light irradiated part is slower * 3. However, the LED itself generates heat, so heat dissipation measures are indispensable. Once the allowable temperature of the LED chip is exceeded, the luminous efficiency of the LED will decrease, which will also adversely affect the life of the bulb.
From the outside, the characteristics of LED bulbs can be said to be the result of improved heat dissipation. Looking at the LED bulb from the side, more than half of the overall lower side is the heat sink (Figure 1). Toshiba Lighting and Sharp both use radiators made of aluminum alloy castings.
Comparing the radiators of the two, in addition to the color, the shape difference is also very obvious. Although there are a few more Sharp products in terms of height, the channel area of ​​the radiator is larger than that of Toshiba Lighting. The channel depth of Toshiba lighting products gradually increases from bottom to top, while Sharp's is basically the same height from top to bottom.
The larger the surface area of ​​the heat sink, the higher the heat dissipation performance. In the case of limited external dimensions, increasing the channel depth is one of the methods to increase the surface area, but as the channel depth increases, the internal installation space of the power circuit board, resin shell, etc. will decrease accordingly * 4.
Toshiba Lighting's radiator has a cylindrical interior space, and Sharp products have a conical shape close to the shape (Figure 2). While maintaining the insulation, the resin shell mounts the power circuit board on the bulb housing.
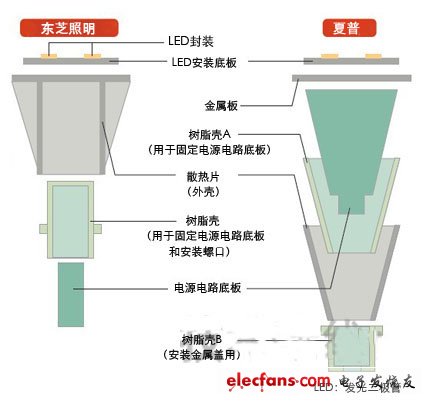
Figure 2: The main structure of the LED bulb. Toshiba Lighting ’s LED bulb radiator (housing) has 16 right-angled triangular channels on the side of the cylinder and is covered with a circular plate. The LED substrate is directly fixed on it. The power circuit board is fixed in a cup-shaped resin case and inserted from below the heat sink. On the other hand, the radiator of Sharp LED bulbs has a tapered cylindrical shape, and 60 blades with a height of less than a few mm are mounted on the surface. The LED substrate is fixed on a disk-shaped metal plate covered above the heat sink. The power circuit board is fixed in a conical (but mostly hollowed out) resin shell A inserted above the heat sink. (click to zoom in)
The LED chip is the largest heat source of the LED bulb. In the bulb, a plurality of LED chips are packaged together and then mounted on a substrate made of aluminum alloy. The aluminum alloy LED substrate is fixed on the upper part of the heat sink. In Sharp's products, a metal plate is also sandwiched between the LED substrate and the heat sink.
This article will introduce the internal structure of the LED bulbs of Toshiba lighting products and Sharp products in detail.
Radiator connection structure is different
The hemispherical part that diffuses the LED light is called "spherical lampshade". Toshiba Lighting's spherical lampshade is made of polycarbonate and is fixed to four positions above the radiator with adhesive. The spherical bulbs of ordinary bulbs are generally made of glass. This is because LED light does not easily generate heat, so resin can be used. Moreover, after using resin, it is not easy to break when the bulb is dropped, thereby improving safety.
Below the spherical lampshade is the LED substrate. Among the products of Toshiba Lighting, among the 6.9W (white, total luminous flux 565lm) rated power consumption products, the number of LED packages on the LED substrate is 7 (Figure 3) * 5.

Figure 3: The back of the upper LED substrate of the Toshiba LED bulb is in contact with the upper surface of the heat sink (housing) and is directly fixed with 2 screws.
Toshiba Lighting's LED substrate is equipped with a connector to connect the power circuit line. The connector is a product that does not require soldering, and it is estimated that the ease of assembly is given priority. Incidentally, the LED bulbs of Toshiba Lighting are assembled in factories in Japan.
The LED substrate is fixed by 2 screws, and the upper surface of the heat sink can be seen after removing the substrate. This part is flattened by mechanical processing, and only the LED substrate is screwed to be fully attached to the back of the substrate to obtain thermal conductivity.
The spherical lampshade of Sharp's LED bulbs is made of glass * 6. 7.5W (daylight color, total luminous flux 560lm) rated power consumption products are equipped with 6 LED packages on the LED substrate (Figure 4). The wiring between the power circuit boards is connected by welding.

Figure 4: The upper LED substrate of the Sharp LED bulb is fixed on the metal plate with 3 screws, and the thermal oil is coated between the two. In addition, the wiring to the power supply circuit board was soldered.
The LED substrate is fixed on the metal plate with 3 screws, and Grease is coated between the two. Fixing the LED substrate is not a heat sink made of aluminum alloy castings, but another metal plate. Although the material is aluminum alloy, the surface does not show any signs of machining. Using this metal plate to fix the LED substrate, the bonding performance of the two may not be sufficient, so it is necessary to use thermal grease.
The metal plate is fixed to the heat sink with 3 screws (not the screws that fix the LED substrate). After removing the metal plate, you can see that the inside of the radiator is filled with black resin (Figure 5) * 7. It is estimated that these resins are filler materials that promote thermal conductivity, but these resins are not in contact with the back of the metal plate, so it is speculated that its main purpose is to conduct the heat of the power circuit board to the heat sink, not the heat emitted by the LED package.
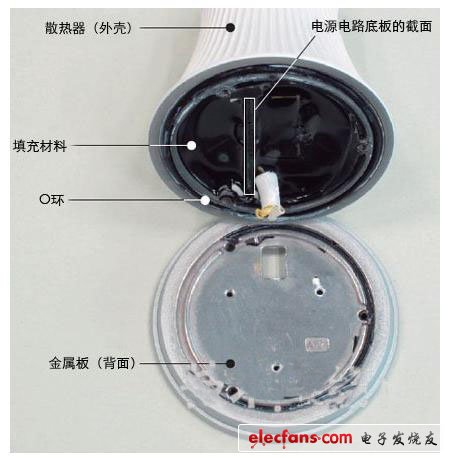

Figure 5: The internal metal plate of the Sharp LED bulb is fixed to the heat sink (housing) with 3 screws. The inside of the radiator is filled with filling material, but it does not contact the back of the metal plate, and heat can only be conducted through the contact portion of the metal plate and the radiator. In addition, an O ring is arranged between the two to ensure airtightness. (click to zoom in)
The contact part of the radiator and the metal plate is ring-shaped, and the area is not large. The contact part on the back of the metal plate has a full circle of flanges, which not only facilitates positioning during assembly, but also slightly expands the contact area. In addition, the outer edge of the metal plate is exposed to the outside of the bulb, which becomes the embellishment of the bulb design.
The purpose of the O-rings arranged around the contact part between the metal plate and the heat sink is unknown. If it is to maintain airtightness, the role of the ring should be to prevent the leakage of the material filled with liquid resin and prevent water from entering from outside. Promoting the conduction of heat from the metal plate to the radiator is also one of the imaginable purposes.
8Dn9 Gas Insulated Metal Enclosed Switchgear
Square D Switchgear,Switchgear For Generator,Metal Switchgear,Siemens Switchgear Products
Shandong Shunkai electrical equipment co., LTD. , https://www.chinasdsk.com