In 2009, under the leadership of KDDI and other operators, 3GPP further enhanced the performance of 1x CSFB in the R9 version, and proposed the e1x CSFB solution. The technical indicators of e1xCSFB, such as voice fallback delay, have been significantly improved. The simulation results show that under this pre-increment version, the delay of voice fallback access to 1x system is close to or even exceeds that of standard 1x terminal access to 1x system. e1xCSFB has two fall-back modes. One is that the voice similar to R8 falls back to the 1x network, and the LTE data is interrupted. The other is that while the voice falls back to the 1x network, the LTE data service is switched to the eHRPD network, which requires 1x / DO. The terminal needs to support concurrent voice and data services. At present, Qualcomm is developing SVDO chips to achieve 1x and DO voice and data concurrency.
In order to cooperate with the work of 3GPP's e1xCSFB, the WG2.2 group of 3GPP2 TSG-C is working on the e1xCSFB air interface specification C.P0097-0 v1.0 (E-UTRAN – CDMA2000 1x ConnecTIvity and Interworking Air InteRFace SpecificaTIon). The specification entered the V & V stage at the Bangkok meeting in January 2010, but as of the Denver meeting in March, a large number of manuscripts were still submitted, and many technical details still need to be discussed before finally entering Extended V & V. As of April 9, 2010, if there is no new manuscript proposed, it will enter the release approval process, and it is expected that the next meeting will enter the official release.
In December 2009, Verizon led the addition of the Dual Rx solution in the 3GPP R9 release. The difference between the Dual Rx scheme and the above two CSFB schemes is that the scheme is aimed at a terminal with dual receivers and a single transmitter. No interoperability function modules and interfaces are required between the networks. The terminal completes all the work between the two networks. Under this solution, there is a problem that the terminal needs to conditionally terminate / interrupt LTE data in response to the 1x registration message, receiving SMS, and 1x paging scenarios.
4 SRVCC
3GPP started to develop the SRVCC for LTE and CDMA 1x network voice continuity specifications at R8. Both R8 and R9 versions have been frozen. In the R10 version, research is currently underway for enhanced SRVCC (eSRVCC). The research scope of eSRVCC is mainly the continuity of voice calls between LTE and 3GPP's 2G / 3G network circuit domain. It does not include non-3GPP CDMA 1x. The eSRVCC research report is reflected in TR23.856, and version 1.0.0 is currently completed.
The main purpose of eSRVCC enhancement research is to reduce the delay of LTE to circuit domain handover. In addition, in the original SRVCC scheme, the anchor point of the call is generally in the VCC AS of IMS. There is a problem that the upper layer session is synchronized with the underlying PS to CS handover. The eSRVCC program will consider solving this problem.
The technical solutions provided by eSRVCC include Huawei, CMCC, NTT, and NEC, etc., which use SGW / PGW as the anchor point for SRVCC voice calls, similar solutions from NSN, and various solutions from other companies. In the next meeting of 3GPP SA2, various solutions will be evaluated in depth.
For the enhancement of LTE-1x RTT eSRVCC, there is also a technical possibility of adopting the SGW / PGW anchoring idea of ​​3GPP eSRVCC.
5 PCC
5.1 PCC enhancement
PCC function enhancement is the subject of 3GPP SA2 project research in 2009. For the PCC of R8 / R9, there are mainly the following four enhancement function requirements:
(1) Third-party data connectivity (Sponsored Data ConnecTIvity) refers to third-party services (non-operator-deployed AF) that supports Rx interfaces and cooperates with the operator ’s PCC architecture to control services, reduce traffic, and charge billing. The implementation of this solution is under discussion, possibly through the enhancement of Rx interface parameters.
(2) Coherent Access to Policy Related Databases: In order to implement the policies formulated by operators, multiple logical databases such as HSS, SPR, and ANDSF-related databases need to be accessed. Currently, 3GPP is working on the specification of unified database UDC in SA5, aiming to logically merge databases and provide a single logical access interface. For the PCC architecture of SA2, one possible idea is that PCRF is used as a front-end application to access UDC data while the user's IP-CAN session is in progress. When the user is not in a session, PCRF does not need to store user data.
(3) QoS Control Based on Spending Limits: PCRF can perform QoS control and gating based on the information obtained from OCS. For example, PCRF can change the user's current QoS level based on the user's consumption limit. A possible solution to the realization of this requirement is enhanced through the Gx / Gy interface. OCS provides charging strategies for the PCRF. As the only policy control node of the network, PCRF uses OCS policy information to formulate and execute PCC policies.
(4) Service Awareness: Identify different services through DPI, so that different strategies can be implemented for different services. At present, the implementation needs to choose between the architecture based on the Rx interface and the Gx interface. Companies such as Huawei and Verizon recommend that the architecture based on the Gx interface be used as the basis (the Rx interface may belong to a third party), and the implementation is enhanced through the Gx interface.
In addition, the following two functional requirements were adopted at the SA2 # 78 meeting in February 2010:
(5) Service-based traffic steering (Service Based Traffic Steering) requirements and solutions are also under discussion. The requirement refers to that when the gateway detects the service type, it chooses to bypass the service data (Offload). At present, the main problem is that the bypass will cause changes in the service IP address and service interruption.
(6) Extending Policy Architecture to Support Interactive Services (Extending Policy Architecture to Handle TransacTIonal Services) means that the existing PCC architecture is only for IP flows and cannot monitor non-IP services such as SMS. Therefore, the existing PCC architecture needs to be expanded.
5.2 Fixed-line mobile convergence PCC
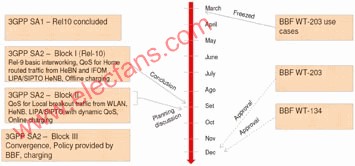
3GPP and BBF established a joint working group at the SA2 # 78 meeting in February 2010 to establish a project to study and integrate PCC. The project has attracted the attention of mainstream operators and equipment vendors in the industry. The progress of BBF and 3GPP project preliminary determination is shown in Figure 1.
 ã€
ã€
Figure 1 BBF-3GPP WID schedule
In the recent plan of the working group, 3GPP SA2 will analyze the capability gap between S9 interfaces for interworking, and report the results to the BBF meeting. BBF WT-203 will provide additional application scenario documents at the BBF Q1 meeting. After the Q1 meeting, application scenarios will no longer be considered.
At present, the following consensus has been reached on the fusion PCC architecture:
(1) The initial interworking scenario is assumed to belong to users of the mobile network.
(2) The feasibility of interworking depends on mobile and fixed-line operators in terms of authentication and QoS, and cooperation agreements.
(3) It is up to 3GPP to decide whether it is necessary to perform integrity protection on the s2c interface.
(4) Pay attention to the scenario where s2a, s2b, and s2c are interconnected.
(5) For networks based on trusted mobility, other protocols besides PMIP should be considered.
(6) SA2 studies the S9 * (PCRF-BPCF) interface based on the S9 interface.
(7) The impact on fixed-line RGs should be minimized.
(8) When the AF uses the S9 * interface, the Rx interface in the BBF is not considered.
Of course, there are many problems to be studied, such as identification in mobility / roaming / nomad, IP address allocation, network discovery and selection; whether AAA cross-domain charging is online or offline, should support tunneling protocols, RADIUS and Diameter Protocol interworking; how BBF in policy and billing relates to 3GPP service data flow and BBF IP flow, S9 interface extension (S9 *), PCRF and BPCF function division, etc.
5.3 3GPP2 PCC
3GPP2 is developing the PCC specification X.P0062 based on CDMA network. The specification is based on the PCC specification of 3GPP R8 in principle, focusing on how to adapt the PCC to the CDMA network. The scope of the specification research includes CDMA 1x and HRPD networks. However, since the 1x network itself has weak support for QoS at interfaces such as air interface and IOS, whether PCC can be used requires further confirmation. At present, the X.P0062 specification has completed the work of architecture and main processes. The overall architecture supports simple IP, MIP, PMIP and other different network architectures, and the charging mode supports offline charging.
6 Conclusion
This article introduces the data interoperability of LTE and CDMA networks, the CSFB of LTE and CDMA network voice interoperability, and the latest standard progress of SRVCC. In addition, the progress of 3GPP and 3GPP2 PCC related standards is introduced.
The LTE and CDMA network data interoperability scheme is currently further refined in the 3GPP2 X.S0057 standard. The remaining problems were improved in X.P0057 version 0 3.0. For the R9 version of 3GPP, 3GPP2 is developing version A of X.P0057. In addition, the industry is studying a fast handover scheme based on non-optimized handover.
For the 3GPP R8 version of the CSFB standard, KDDI and Verizon proposed new requirements and solutions respectively in 2009, corresponding to e1xCSFB and Dual Radio 1xCSFB. In the implementation process of the tunnel interface, the former optimizes the fallback process of R8 by introducing the switching process of SRVCC, thereby reducing the delay. The latter achieves fallback by supporting dual receivers on the terminal, simplifying the interoperable network structure.
For the SRVCC enhancement needs of China Mobile and other operators, the 3GPP R10 version is in the process of researching and optimizing the SRVCC solution. The SRVCC enhancement for CDMA is currently not specifically researched.
As the hotspot of industry research, PCC is currently developing enhanced PCC in 3GPP R10. In addition to the four functional requirements such as DPI-based deep packet inspection, recently, business-based traffic orientation and an extended strategy architecture have been proposed to support the two functional requirements of interactive services. In addition, 3GPP is working with BBF to establish a project to study FMC's PCC. 3GPP2 is also developing CDMA PCC based on 3GPP's R8 PCC.
Track the latest development of 3GPP2 and 3GPP CDMA and LTE interoperability related hotspot issues, including LTE and eHRPD data service interoperability and LTE and CDMA 1x voice 1x CSFB and SRVCC standards, follow up the research results of 3GPP PCC enhancement work .
1 Introduction
The evolved packet system EPS (including E-UTRAN and EPC) is the main choice for mobile operators' future network evolution. For CDMA operators, after the introduction of EPS networks in the future, there will be business interoperability issues between E-UTRAN and CDMA packet and circuit domains .
Interoperability between EPS and other non-3GPP networks (including CDMA) is defined in the 3GPP TS23.402 standard. The 3GPP2 X.S0057 standard further refines the implementation plan and implements non-real-time and real-time data service interoperability with EPS through eHRPD . At present, there are many new and different versions of X.P0057 for 3GPP R9 and the remaining problems. Although there are two options for data service interoperability: optimized handover and non-optimized handover, at this stage, more operators only consider non-optimized handover.
Since the initial coverage and performance of the E-UTRAN network deployment may not necessarily deploy real-time services, even if the real-time services are deployed, there may be problems such as voice continuity, so in the 3GPP R8 version, we began to develop voice services based on E-UTRAN and CDMA 1x CS. Operating scheme, namely the CSFB specification of TS23.272 and the SRVCC specification of TS23.216. Among them, CSFB, as a simplified transitional voice solution, has nothing to do with the IMS network and does not require E-UTRAN to have VoIP capabilities. The design idea requires that users can answer / initiate 1xCS when performing data services on the E-UTRAN network. Services such as voice calls and SMS. SRVCC is more suitable for operators deploying IMS. The VCC AS of IMS can ensure the continuity of voice services. With the ever-changing needs of operators and the deepening of standards research, e1xCSFB and Dual RADIo 1xCSFB were added to the new requirements of KDDI and Verizon in the R9 version. The 3GPP R10 release has also begun to study and optimize the SRVCC solution for the enhanced SRVCC needs of operators such as China Mobile.
PCC is another research hotspot in the industry and the main means for operators to differentiate their operations. After the 3GPP R8 version was proposed, after further research in the R9 version, 3GPP is currently developing enhanced PCC (ePCC) based on R10, including 4 enhanced functions including deep packet inspection (DPI). In addition, the joint research of 3GPP and BBF is based on PCC of FMC. 3GPP2 is also developing CDMA PCC based on 3GPP R8 PCC.
This article tracks the progress of LTE and eHRPD data service interoperability standards, LTE and CDMA 1x voice 1x CSFB, e1xCSFB, Dual radio 1x CSFB and SRVCC / eSRVCC standards. In addition, the latest progress of 3GPP enhanced PCC and 3GPP2's CDMA PCC progress were tracked and studied.
2 LTE and eHRPD data interoperability
The data interoperability between LTE and eHRPD is formulated in the 3GPP TS23.402 and 3GPP2 X.S0057 standards. Currently, the latest versions of the 3GPP2 specifications are X.P0057 Rev0 v3.0 and X.P0057 Rev A v0.
X.P0057 Rev A v0 has been studied since the Hawaii conference in 2009. The goal is to align with 3GPP R9. Therefore, several functions of 3GPP R9 have become the main research content of this version, such as MAPSUP. X.P0057 Rev0 v3.0 started research at the Bangkok meeting in January 2010, focusing on solving the remaining problems of interoperability.
At present, the main issues discussed in data interoperability are related to the technical details of QoS initiated by the eHRPD network, the new function requirements of the Pi * interface during HSGW handover, the eHRPD network supports the PDN-ID identification of MAPSUP, the optimized MME after the handover informs eHRPD to delete resources, etc. And clarify some PDN IP address issues, etc.
In addition to standard work, the industry is also considering further optimization solutions for data interoperability from LTE to eHRPD. At present, the independence of the two networks can still be maintained when conducting major research ideas. Under the premise of deploying tunnel interaction, through the dual-mode dual-receiver terminal and assist in the optimization of some processes. The main process optimization reflects that the terminal pre-registers in the eHRPD network first, so as to effectively save the switching time when LTE is switched to the eHRPD network. The test performance of this scheme is between non-optimized handover and tunnel-based optimized handover scheme.
3 CSFB
3GPP started to formulate a voice interoperability solution for LTE and CDMA 1x networks in the R8 version-1x CSFB, that is, it can ensure the initiation and reception of 1x CS voice services while connecting or residing in the LTE network. The solution is aimed at Single Radio's single-receiver and single-transmitter terminals. There is an interoperability function module (IWS) and interface (S102) between the LTE network and the 1x network.
Globe string light set is waterproof and durable. Can be used in any season and many applications such as wedding, party, garden etc. We have different wire model and Replacement Bulb type to choose.
Decorative string lights are not just for holidays anymore . Instantly transform indoor and outdoor spaces with a wide selection of covers and finishes that match current trends and personal tastes and expressions.
Celebrate any season ,event or inspired whim with a charming new set of outdoor string lights!
Led Globe String Lights,Plastic Bulb Globe String Lights,Frosted Bulb String Lights,String Lights Large Bulbs
DONGGUAN JIANXING LIGHTING ELECTRIC APPLIANCES CO., LTD , https://www.rslightstring.com