Sound refers to other sounds besides human language and music, including the sound of the natural environment, the sound of animals, the sound of machine tools, various sounds made by human actions, etc.
The sound probably includes a set of power amplifier, peripheral equipment (including compressor, effector, equalizer, VCD, DVD, etc.), speakers (speakers, speakers), mixer, microphone, display equipment, etc. Among them, speakers are sound output devices, speakers, subwoofers and so on. A loudspeaker includes three types of speakers: high, low, and medium, three but not necessarily three. The development history of technology can be divided into four stages: electron tube, transistor, integrated circuit, and field effect tube.
Sound componentAudio equipment probably includes power amplifiers, peripheral equipment (including compressors, effects, equalizers, exciters, etc.), speakers (speakers, speakers), mixers, sound sources (such as microphones, musical instruments, VCD, DVD) display equipment Wait to add up. Among them, speakers are sound output devices, speakers, subwoofers, etc., a speaker includes high, low, and middle speakers, three but not necessarily three.
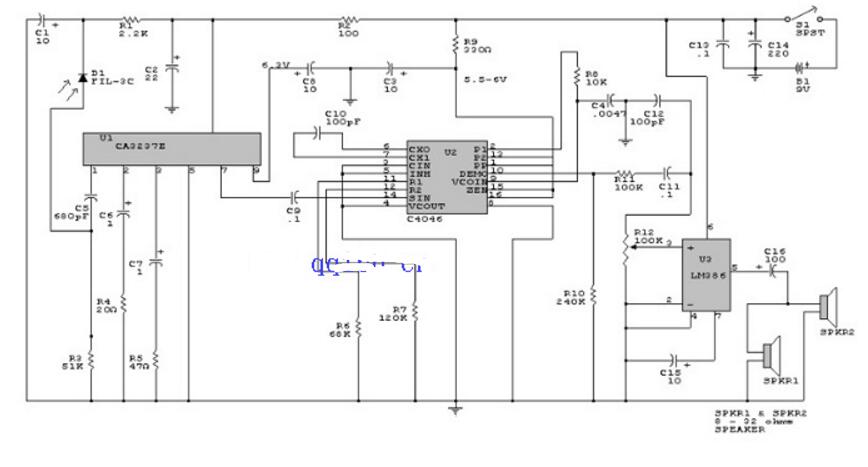
Audio circuit schematic
How the speaker worksTo understand the principle of sound produced by the speaker, we first need to understand the propagation of sound. The propagation of sound requires a medium (vacuum cannot transmit sound); the sound must rely on all gases, liquids, and solids to spread out as a medium. These substances as a medium of transmission are called media. Just like a water wave, you throw a stone on the calm water, and there is a wave on the water surface, and then propagate to the other side for 4 weeks; the sound wave is also formed in this way. The frequency of the sound wave is in the range of 20-20,000 Hz, and can be heard by the human ear; below or above this range, the human ear cannot hear. Waves and sound waves propagate in the same way. Only through the propagation of the medium can the human ear hear the sound. Sound waves can propagate in gases, solids, and liquids.

Let me talk about the working principle of the speaker. A horn is a device that converts electrical signals into acoustic signals. It consists of coils, magnets, paper cones, etc. The current (alternating current) of different sizes output by the amplifier moves the coil under the action of the magnetic field through the coil. The coil is connected to the paper cone to drive the paper cone to vibrate, and then the vibration of the paper cone pushes the air to make a sound.
The sound principle of the horn
When the speaker receives the electrical signal output by the sound source device, the current will pass through the coil on the speaker and generate a magnetic field reaction. The current through the coil is an alternating current, and its positive and negative poles are constantly changing; the positive and negative poles will attract each other, and the coil will be attracted by the magnet on the horn to move backward (in the box); the positive pole and the positive pole will repel each other. , The coil moves outward (outside the box). This expanded rhythm will produce sound waves and air currents, and emit sound, which has the same effect as the throat vibration of our speech.
Frequency response curve SPLvsFreq
The frequency range that can be heard by the human ear is 20Hz-20KHz, ("20hz is called infrasound," 20KHz is called ultrasound). The vertical axis of the icon-represents the sound pressure level, and the unit is dB. The abscissa of the icon means frequency, the unit is Hz.
The picture above shows the frequency response curve of the bass unit, and the tweeter unit on the right side, including the left and right speakers. Several important parameters can be known from the frequency response curve:
Characteristic sensitivity (SPL): The sound pressure measured at a distance of one meter with one watt of electric power, and the average value obtained from four points from the frequency response curve is the average sound pressure.
Effective frequency range (F0 ~ 20KHz): It can be SPL-10dB, so that a straight line and a curve intersect two points, and the effective frequency range is between these two points. As shown above, the effective frequency range of the speaker is 45Hz ─ 20KHz, the effective frequency range of the bass unit is 40Hz ─ 3KHz, and the effective frequency range of the tweeter unit is 1800Hz ─ 20KHz. The flatter the frequency response curve, the better, and the wider the bandwidth, the better.
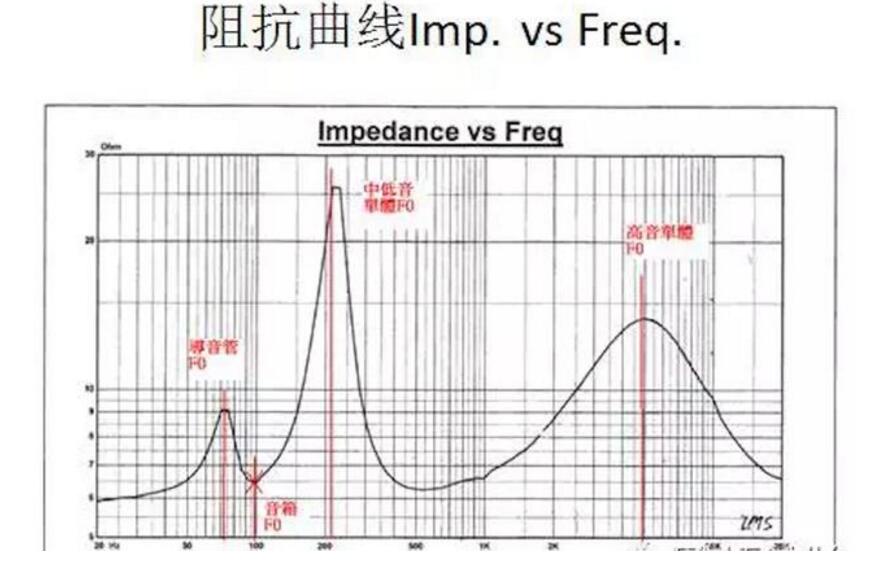
Several important parameters can be known from the impedance curve:
Impedance value (Ohm):
The lowest coordinate corresponding to the lowest point after the peak of the graph is the impedance value.
Minimum resonance frequency (F0):
Single speaker (single peak) ─The point where the peak of the impedance curve corresponds to the abscissa is F0. Speaker horn (double peak)-The point on the abscissa corresponding to the valley between the first peak and the second peak of the impedance curve is Fb, the first peak is the sound tube F0, and the second peak is the single F0. Speaker speaker + tweeter (three peaks)-the point where the peak of the impedance curve and the valley between the peaks corresponds to the abscissa is Fb, and the third peak is F0 of the tweeter.
1. DC impedance (Ohm):
The impedance is measured with a static speaker, so the result is the DC impedance, which is the impedance value of the total length of the copper wire wound on the voice coil. DC impedance is not affected by frequency.
2. AC impedance (Ohm):
The dynamic impedance, that is, the AC impedance value obtained after power-on.
(Typically, the tolerance of the voice coil is ± 15%.)
3. Standard input power (W): is the rated withstand power of the speaker, which is a guaranteed value.
4. Maximum input power (W): refers to the maximum withstand power of the speaker, only withstand the peak voltage within 1 second, non-guaranteed value.
5. Output sound pressure, also known as sensitivity (dB):
Sensitivity, also called characteristic sensitivity, is generally defined as the sound pressure generated on the reference axis at one meter from the reference point when the speaker is placed on the input of the anechoic chamber baffle plus a signal voltage equivalent to one watt of electrical power at rated impedance , The characteristic sensitivity is expressed in decibel "(dB)" units. The sensitivity of the speaker has a greater relationship with the performance of the speaker vibration system and the magnitude of the magnetic induction in the air gap.
6. Polarity:
Add a pulsed DC signal to the input terminal of the speaker. If the vibration is pushed forward, the positive terminal of the speaker is connected to the positive terminal of the DC voltage, and the negative terminal is the reverse.
Cable Type Switching Current Transformer
Cable Type Switching Current Transformer,Low Voltage Outdoor Transformer,Zero Sequences Current Transformer,Split Core Zero Sequence Current Transformer
Zibo Tongyue Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.tongyueelectron.com